- Computer Networks operation principle is similar in many aspects to that of postal networks, in that both use next hop routing and not end-to-end routing. Also there is no concept of end-to-end circuit reservation in both these networks.
- Each communicating computer need to have at least one IP address to uniquely idenltify it in the network
- Data is split into smaller units called packets and transferred using packet switching. A packet header encapsulation enables each packet to be independently routed through the underlying computer network.
- At every hop, next hop routing is used to identify a suitable neighbor, that is closer to the destination computer, to pass on the packet in its journey from the source computer to the destination computer.
- Each telecommunication link that is part of the data exchange is not reserved for specific packets and is usually shared between packets belonging to different sessions.
- Data Link layer and physical layer are together used to carry a packet to the next hop (neighboring computer)?
- Actual data communication between next hop neighboring computers happens at the physical layer through transmission of appropirate electrical/electromagnetic/optical signals
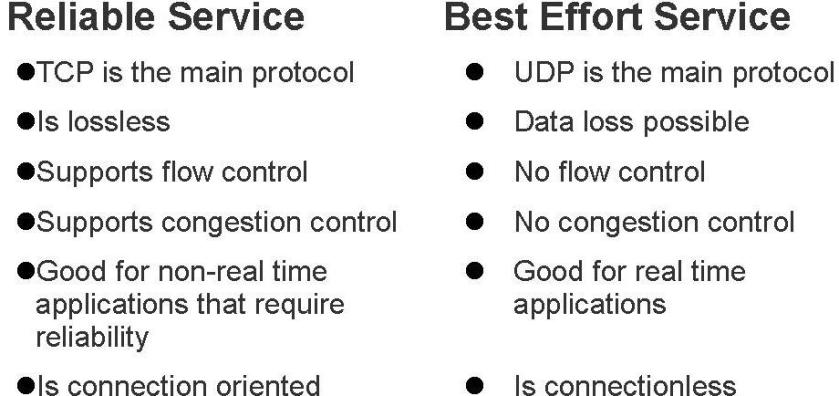
- Computer networks primarily provide two types of services to the application. They are i) a reliable byte stream oriented service and ii) an unreliable best effort message oriented service.
- Layering in computer networks helps in maintaining modularity and simplicity to the whole operation. Hybrid layering model is the one that is practically used.
Some thumb rules for basic computer networking operation
Lists out some basic attributes of computer networking including similarity to postal networks, packet switching, next-hop routing, layering and types of services.