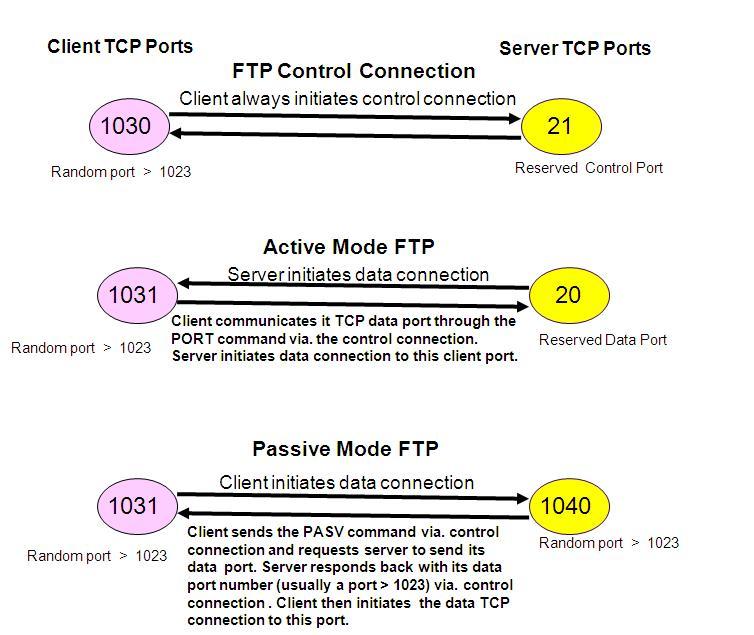
In FTP, the control TCP connection is always initiated by the FTP client to the FTP server, with the FTP server always waiting on the standard TCP reserved port number 21. The variation comes only in who initiates the TCP data connection, to be used for file transfers.
If the server initiates the TCP data connection to the client, then it is classified as Active Mode FTP (as the server is active in initiating the connection). In this mode, the client communicates its data port via. the already established control connection using the PORT command. It then does a passive open on this data port and waits for the server to initiate the data connection. The server then initiates a new TCP connection to the client on this port. Active Mode FTP is the default mode.
If the client initiates the TCP data connection to the server, then it is classified as Passive Mode FTP. In this mode, the client sends a PASV command via. the control connection, requesting the server to communicate its data port. The server then does a passive open on a new random port and sends the port number to the client via. the control connection. The client then initiates a new TCP connection to the server on this port, to be used for data transfer purposes.
The figure below illustrates both active and passive modes:
Firewall Implications
In the active ftp mode, since the client has to allow data connections from servers onto one of its high data ports (> 1023), its firewall has to be configured to allow such connections from any remote server. Hence, the active ftp mode is not favorable to the client. Similarly, going by the same argument, the passive ftp mode is not favorable to the server, as its firewall has to be configured to allow data connections on high random ports from any external client.
Requirement of NAT and Firewall ALGs for FTP
In FTP, while the control connection is always initiated to a standard reserved destination port of 21, the destination port for the data connections are dynamically chosen, through command exchanges on the control connection. This means that the NAT and firewall configurations at the client and server ends need to be made aware of these dynamic data connections, each time a new data connection happens. That is why a separate NAT ALG (Application Level Gateway) and another separate Firewall ALG are required for the FTP protocol.
The role of the FTP NAT ALG is to monitor the control connection for exchange of dynamic data ports (via. the PORT/PASV commands) and then dynamically add new entries to the NAT table for translating data connections. Such dynamically added entries should be automatically removed from the NAT table as soon as the TCP data connections are closed (typically after a file transfer).
The role of the FTP Firewall ALG is to monitor the control connection for exchange of dynamic data ports and then add rules dynamically in the firewall table to allow data connections on these ports. Such dynamically added entries should be automatically removed from the Firewall table as soon as the TCP data connections are closed.